Remote Equipment Probing and Monitoring |
Remote equipment probing and monitoring is the base of remote control and/or e-diagnosis. In many cases, the equipments that need to be probed are widely scattered in many places, usually several miles away from the control center.
|
|
The conventional ways
For off-site equipment with self-testing features:
- Scheduled self-testing, real-time data transmission to database at control center, scheduled result monitoring at control center.
- Scheduled self-testing, real-time data transmission to database at field, scheduled result monitoring at control center.
For off-site equipment without self-testing features:
- Staff needs to bring testing equipment to testing sites for regular check rounds.
- Control center needs to run testing programs periodically to check off-site plant status.
|
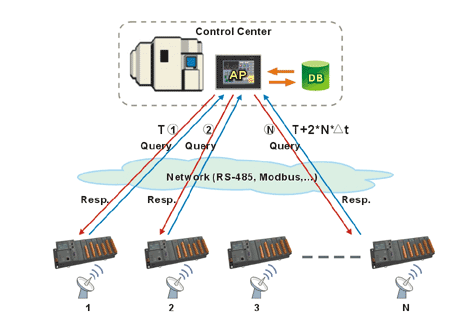 Figure 1. Remote Equipment Probing and Monitoring in conventional ways |
These conventional ways have several serious defects: |
- Delay in result collection, limited space in Field database and high level of weather resistance is required.
- Massive waste in bandwidth and run time. The more check points are, the worse the delay is.
|
The iPush� Embedded ways
For off-site equipment with self-testing features:
- Equipments self-test periodically and transmitting result through iPushR Embedded back to the control center in real-time, and store it into database at the same time.
For off-site equipment without self-testing features:
- Install testing program into WinCon-8000 for scheduled testing and send real-time result back to control center.
|
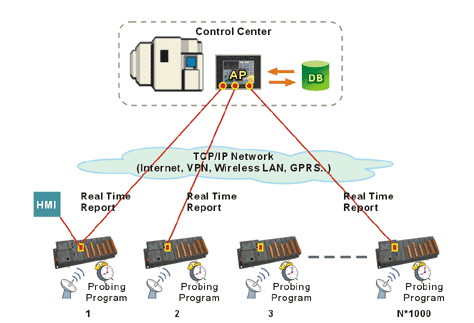 Figure 2. Remote Equipment Probing and Monitoring in iPush® Embedded ways with scheduled testing |
Otherwise, staff can also run the testing program on WinCon-8000 to get real-time result and send the data back to control center through iPushR Embedded. |
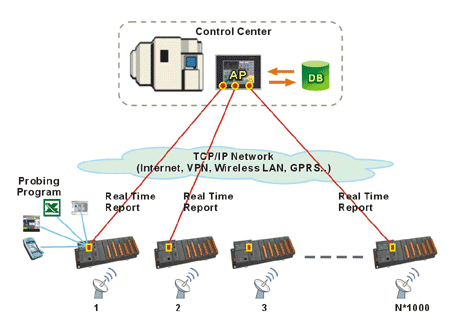 Figure 3. Remote Equipment Probing and Monitoring in iPush® Embedded ways under control center's command |
Benefits with iPushR Embedded in WinCon-8000
- When abnormal results occur, real-time alarm notification prevents further damage.
- Control center receive real-time test result.
- Does not have to repeat handshaking and transmitting, so it will saves huge amount of bandwidth and time.
Examples
- Civil Defense: Air-alert broadcasting network equipments monitoring.
- Hydraulic engineering: Dam sluicing alert broadcasting network equipments monitoring.
- Telecom: Scattered unmanned facilities monitoring system.
- Water, gas pipelines: Urban pipelines instruments and/or control equipments monitoring.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing equipments monitoring.
- Power industry: High-voltage power equipments (e.g. power line, connector, transformer, substation, !Ketc.).
|



